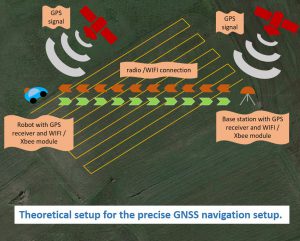
With this post I will explain how a theoretical setup of a precise GNSS positioning architecture could look like. One essential part of the setup is the GPS base station. The base station knows her own position to less than a few centimeters exact. The mobile unit respectively the robot car is also equipped with a GPS system and know his dynamical position imprecise for a few meters. So that the mobile unit also know his position very precise the failure of the deviation received form the GPS signal has to be calculated. To make the calculation of the deviation possible the base station and the mobile unit has to be connected via radio. This radio connection has to be very fast otherwise the calculation of the deviation will not be as accurate as possible depending of the latency of the signal. The setup of the precise GNSS solution with a base station and mobile unit looks like as illustrated in the picture below.
Where does the deviations in the GPS positioning come from?
This type of deviations in the GPS signal are intended by the army and disturbances in the atmosphere affect the GPS signal in a negative way. The various active GPS systems are mainly developed for a military usage and the military does not want that everybody could use their system at a maximum of accuracy. Only the army of each system they developed is able to use their GPS system with a maximum of accuracy. On the other hand deviations take place by the long distance between the satellite and the receiver on the ground. Different air masses in the stratosphere and ionosphere through which the signal spread through result in a week signal. As well reflections on trees, along a deep valley or in a town with high buildings could result as well in deviations in the received GPS signal. All this errors and problems the radio signal has result in a vague absolute GPS position of your base station and mobile unit.
How does the correction of the GPS position works?
The correction of the error in the received GPS signal is done by the RTK library. This library processes the data and with complex calculations the exact position of the mobile unit is calculated in the program RTKRCV. This calculations needs a few minutes and enough valid satellites. Otherwise it could take up to a few hours to calculate the exact position. The time the RTK library needs depends from the number of valid satellites and how good the GPS signal is received. If the base station and mobile unit receives enough valid satellites the system is very fast ready for use and the mobile unit is feed with the absolute GPS position. Important for the setup is the radio link between the base station and the mobile unit which enables the system to correct the vague position of the mobile unit. It is important the radio link is very fast. It has to be very fast because a slow connection over a long distance results at the end in a week corrected GPS position which is received by the mobile unit. More about the RTK library and how does the library works is explained on the project web site of the RTK library.
Homepage: An Open Source Program Package for GNSS Positioning RTKLIB
Technical setup with the RasPiGNSS module
The technical setup is very fast explained. You need in the base station and in the mobile unit a RasPiGNSS Aldebaran module from www.drfasching.at. He offers via his online shop the modules and GPS antennas I used for the setup explained on my blog. The RasPiGNSS module is attached on top of the 40 pins of the Raspberry Pi. For the radio link between the base station and mobile unit a XBee Pro module is used. But for the first test a WIFI connection is fast enough. The XBee Pro modules are connected to the Raspberry Pi via an XBee USB adapter. The XBee Pro modules are working with a 2 GHZ frequent and this enables the modules to communicate over a distance of a few hundred meters. I bought the XBee Pro S1 modules with an external antenna connector. This is perfect because with an external antenna the range of the radio connection is extended. As operation system I am using Raspbian Jessie. This are all the important components you need for the differential GPS setup.
The picture below shows the RasPiGNSS Aldebaran module mounted on top of the Raspberry Pi.
Article list - GPS module RasPiGNSS:
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – introductionPrecise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – theoretical setup
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – GPS antenna setup
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – software installation
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – configuration RTKLIB base station
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – configuration RTKLIB mobile unit
Precise GPS GNSS positioning with a Raspberry Pi and the RTKLIB – XBee serial data transmission










Ingmar, thanks for putting all your work out here! I’m interested in building a differential GNSS system to use for terrain mapping. Did you test your DGNSS system to characterize the accuracy you are getting? I’d be interested in the altitude accuracy as well, as I’ve heard that GPS is less accurate in the vertical direction. Thanks!